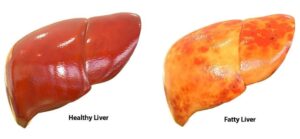
Revitalize Your Liver with Milk Thistle
Steatosis, a condition in which fat builds up in liver cells, is becoming more common, affecting millions of people globally. One natural remedy that is gaining attention for its potential to combat this condition is milk thistle. In this comprehensive guide, we look at the benefits, use, and effectiveness of milk thistle in the treatment of fatty liver disease.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
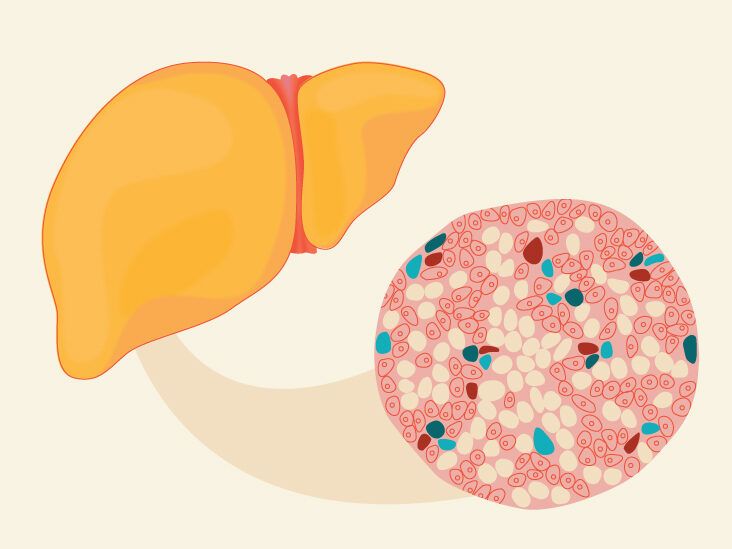
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. This excess fat can interfere with liver function and lead to various health complications if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with fatty liver disease is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is a common cause of fatty liver disease. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to alcoholic fatty liver disease, which ranges from simple fatty liver to more severe conditions like alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis;
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: Obesity and metabolic syndrome, characterized by insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and abnormal lipid levels, are major contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions, from simple fatty liver to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure;
- Medications and Toxins: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, tamoxifen, and methotrexate, as well as exposure to environmental toxins, can cause or exacerbate fatty liver disease;
- Other Factors: Other factors that may contribute to fatty liver disease include viral hepatitis infections (such as hepatitis C), rapid weight loss, malnutrition, and genetic predisposition.
Fatty liver disease is a prevalent condition that can have serious implications for liver health and overall well-being. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition effectively. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing complications and preserving liver function. If you suspect you may have fatty liver disease or are at risk, consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and guidance.
Introducing Milk Thistle

Milk thistle, scientifically known as Silybum marianum, is a flowering herb native to the Mediterranean region but now found throughout the world. It has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various ailments, particularly those related to the liver
- The active compound in milk thistle is silymarin, a flavonoid complex with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Silymarin is believed to be the key component responsible for milk thistle’s medicinal effects. It is known for its ability to protect liver cells from damage caused by toxins and free radicals, as well as to promote liver regeneration;
- Milk thistle is commonly used as a complementary treatment for liver conditions such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and fatty liver disease. It is also believed to support liver detoxification processes and aid in the digestion of fats;
- In addition to its liver-protective properties, milk thistle has also been studied for its potential benefits in managing other health issues, including diabetes, high cholesterol, and certain types of cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness in these areas.
Milk thistle supplements are widely available in various forms, including capsules, extracts, and teas. It is generally considered safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses, but as with any supplement, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Benefits of Milk Thistle for Fatty Liver
Milk thistle is often touted for its potential benefits in the management of fatty liver disease, also known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Here are some ways in which milk thistle may offer benefits for individuals with fatty liver:
- Liver Protection: The active compound in milk thistle, silymarin, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that help protect liver cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation. This protection can be particularly beneficial for individuals with fatty liver disease, where liver cells may be under increased stress due to the accumulation of fat;
- Promotion of Liver Regeneration: Silymarin has been found to stimulate liver cell regeneration, which can help repair damage caused by fatty liver disease and improve overall liver function;
- Reduction of Liver Enzymes: Some studies have suggested that milk thistle supplementation may help reduce levels of liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), which are markers of liver damage. Lowering these enzyme levels can indicate improvement in liver health;
- Antioxidant Effects: The antioxidant properties of milk thistle may help reduce oxidative stress in the liver, which is believed to contribute to the progression of fatty liver disease;
- Improvement in Insulin Sensitivity: Fatty liver disease is closely linked to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Some research suggests that milk thistle may help improve insulin sensitivity, which could be beneficial for individuals with fatty liver disease, especially those with underlying insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes;
- Potential Reduction in Liver Fat: While more research is needed, some studies have indicated that milk thistle supplementation may lead to a reduction in liver fat accumulation, which is a hallmark feature of fatty liver disease.
It’s important to note that while milk thistle shows promise in the management of fatty liver disease, more high-quality clinical trials are needed to fully establish its effectiveness and optimal dosage. Additionally, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Using Milk Thistle for Fatty Liver
Using milk thistle for fatty liver typically involves taking milk thistle supplements, which are widely available in various forms such as capsules, extracts, and teas. Here are some general guidelines for using milk thistle for fatty liver:
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Before starting any new supplement regimen, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have fatty liver disease or other underlying health conditions. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health needs and help determine whether milk thistle is appropriate for you;
- Choose a Quality Supplement: When selecting a milk thistle supplement, look for products that contain standardized extracts with a high concentration of silymarin, the active compound in milk thistle. Quality and purity are important factors, so choose supplements from reputable brands that adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP);
- Follow Recommended Dosage: The appropriate dosage of milk thistle can vary depending on factors such as age, weight, and overall health. Follow the recommended dosage instructions provided on the supplement packaging or as advised by your healthcare provider. It’s important not to exceed the recommended dosage without medical supervision;
- Consistency is Key: Consistency is important when using milk thistle for fatty liver. Take the supplement regularly as directed to maximize its potential benefits. It may take several weeks or months of consistent use to see noticeable improvements in liver health;
- Monitor Liver Enzymes: If you have fatty liver disease, your healthcare provider may monitor your liver enzyme levels periodically to assess liver function. Keep track of any changes in liver enzyme levels while taking milk thistle, and report them to your healthcare provider;
- Lifestyle Modifications: While milk thistle may offer benefits for fatty liver, it is not a substitute for healthy lifestyle habits. Make sure to incorporate other lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, weight management, and avoiding alcohol to support liver health;
- Be Patient: It’s important to be patient when using milk thistle for fatty liver. While some people may experience improvements relatively quickly, others may require more time to see results. Stay consistent with your supplementation and monitor your progress over time;
- Watch for Side Effects: Milk thistle is generally considered safe for most people when taken at recommended dosages. However, some individuals may experience side effects such as gastrointestinal upset or allergic reactions. If you experience any adverse reactions while taking milk thistle, discontinue use and consult with your healthcare provider.
By following these guidelines and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can incorporate milk thistle into your overall approach to managing fatty liver disease effectively.
Effectiveness and Research
Numerous studies have investigated the effectiveness of milk thistle in managing fatty liver disease. While some research suggests potential benefits, including reduced liver enzyme levels and improved liver function, further large-scale clinical trials are needed to establish conclusive evidence.
Precautions and Considerations
When considering the use of milk thistle for fatty liver or any other health condition, it’s important to keep the following precautions and considerations in mind:
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or are taking medications. Milk thistle may interact with certain medications or medical conditions;
- Allergic Reactions: Individuals with allergies to plants in the Asteraceae/Compositae family (such as ragweed, chrysanthemums, marigolds, and daisies) may be at increased risk of allergic reactions to milk thistle. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing;
- Potential Interactions: Milk thistle may interact with certain medications, including but not limited to anticoagulants (blood thinners), antiplatelet drugs, antipsychotic medications, certain cancer drugs, hormone therapies, and medications metabolized by the liver. It may also affect the efficacy of oral contraceptives. Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbs you are taking to avoid potential interactions;
- Not a Substitute for Medical Treatment: While milk thistle may offer potential benefits for liver health, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If you have been diagnosed with fatty liver disease or any other liver condition, follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and management, which may include lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring;
- Quality and Purity: Choose milk thistle supplements from reputable brands that adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP) and undergo third-party testing for quality and purity. Look for standardized extracts with a high concentration of silymarin, the active compound in milk thistle;
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should exercise caution when considering the use of milk thistle supplements. Limited research is available on the safety of milk thistle during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before use;
- Side Effects: While milk thistle is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as gastrointestinal upset, including diarrhea, nausea, indigestion, or bloating. If you experience persistent or severe side effects, discontinue use and consult with your healthcare provider;
- Long-Term Use: The safety of long-term or high-dose use of milk thistle supplements has not been well studied. Avoid prolonged use without medical supervision, and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
By taking these precautions and considerations into account, you can use milk thistle safely and effectively as part of your approach to managing fatty liver or other health conditions. Always prioritize communication with your healthcare provider to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion
Milk thistle holds promise as a natural remedy for fatty liver disease, thanks to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and liver-protective properties. While more research is needed to fully elucidate its efficacy, incorporating milk thistle into a comprehensive approach to liver health may offer benefits for individuals with fatty liver disease. As always, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your health regimen.