Decoding NAFLD: Risks & Remedies
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) poses a significant threat to public health, with its prevalence on the rise globally. Despite its name, NAFLD isn’t exclusive to heavy drinkers; rather, it affects individuals who consume little to no alcohol. This condition starts insidiously, often without overt symptoms, but its consequences can be severe if left unchecked. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nuances of NAFLD: understanding its symptoms, identifying its root causes, exploring treatment options, and advocating for lifestyle modifications crucial in managing this condition effectively.
By arming ourselves with knowledge and proactive measures, we empower individuals to take charge of their liver health and mitigate the risks associated with NAFLD.
NAFLD Symptoms
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is notorious for its silent progression, making early detection a challenge. Initially, individuals may experience vague symptoms or none at all, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment initiation. However, as NAFLD advances, it manifests through various distress signals, including:
- Persistent Fatigue: Unexplained and persistent fatigue, surpassing normal tiredness, could signal underlying liver dysfunction;
- Abdominal Discomfort: Individuals may experience dull or aching pain in the upper right abdomen, indicative of liver involvement;
- Abdominal Swelling: Ascites, characterized by abdominal bloating due to fluid accumulation, may develop in advanced stages of NAFLD;
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, or jaundice, suggests significant liver damage and warrants immediate medical attention.
Recognizing these symptoms promptly is paramount, facilitating early intervention and preventing disease progression.
Causes of NAFLD
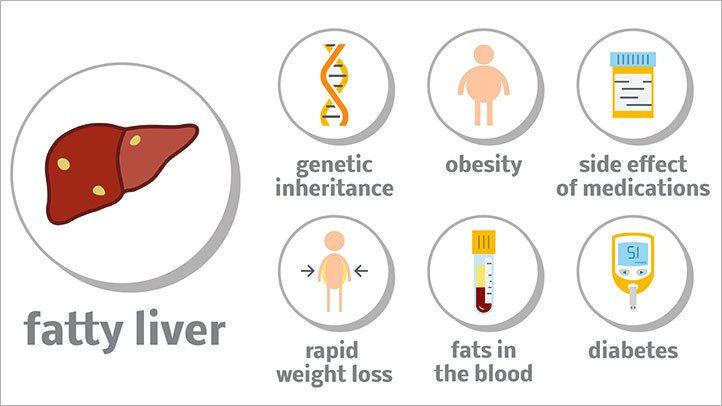
Understanding the multifaceted etiology of NAFLD is crucial in devising targeted preventive strategies. Key factors contributing to NAFLD development include:
- Obesity: Excessive adiposity, particularly visceral fat deposition, significantly elevates the risk of NAFLD by promoting hepatic lipid accumulation;
- Insulin Resistance: Impaired insulin sensitivity exacerbates hepatic fat deposition, fostering the progression from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH);
- Poor Dietary Choices: Consumption of high-calorie, processed foods rich in sugars and saturated fats promotes hepatic lipogenesis, fueling NAFLD pathogenesis;
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity perpetuates metabolic dysfunction, exacerbating obesity and insulin resistance, thereby amplifying NAFLD risk;
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetic variants influencing lipid metabolism and insulin signaling pathways confer susceptibility to NAFLD, underscoring the interplay between genetic and environmental factors.
By addressing these modifiable risk factors through targeted interventions, individuals can mitigate their susceptibility to NAFLD and its associated complications.
Possible Treatments for NAFLD
While no universal remedy exists for NAFLD, adopting a multifaceted approach is imperative in curbing disease progression and restoring liver health. Effective treatment modalities encompass:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Implementing dietary modifications and engaging in regular physical activity constitute the cornerstone of NAFLD management, fostering sustained weight loss and metabolic improvements;
- Pharmacotherapy: Although specific pharmacological agents for NAFLD remain limited, managing comorbid conditions such as diabetes and dyslipidemia is paramount in ameliorating disease severity;
- Advanced Therapies: Individuals with advanced NAFLD, such as NASH or cirrhosis, may benefit from emerging therapeutic modalities, including novel medications and surgical interventions like liver transplantation.
By embracing these interventions and fostering a collaborative partnership with healthcare providers, individuals can navigate the complexities of NAFLD management effectively, safeguarding liver health and enhancing overall well-being.
Conclusion
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease represents a burgeoning public health challenge, underscoring the imperative of proactive management strategies and targeted interventions. By fostering awareness regarding NAFLD symptoms, elucidating its underlying causes, and advocating for lifestyle modifications, we empower individuals to take decisive steps in safeguarding their liver health and mitigating the risks associated with this insidious condition. Through collaborative efforts between healthcare providers and patients, we can forge a path towards comprehensive NAFLD management, thereby enhancing the quality of life and fostering long-term liver wellness.
FAQ
Yes, dietary modifications, coupled with lifestyle changes, can significantly ameliorate NAFLD severity by reducing hepatic fat accumulation and improving metabolic parameters.
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week is advisable for individuals with NAFLD, promoting weight loss and metabolic health.
While NAFLD predominantly affects individuals with obesity, it can also occur in lean individuals, particularly those with central adiposity or metabolic derangements.
Yes, NAFLD can culminate in severe complications such as NASH, cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma, necessitating vigilant monitoring and comprehensive management approaches.