Prozac & Fatty Liver: Unraveling the Connection
In recent years, there has been growing concern about the potential link between the use of Prozac (fluoxetine) and the development of fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease, characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. In this article, we’ll delve into the connection between Prozac and fatty liver disease, examining the risks, prevention strategies, and management options.
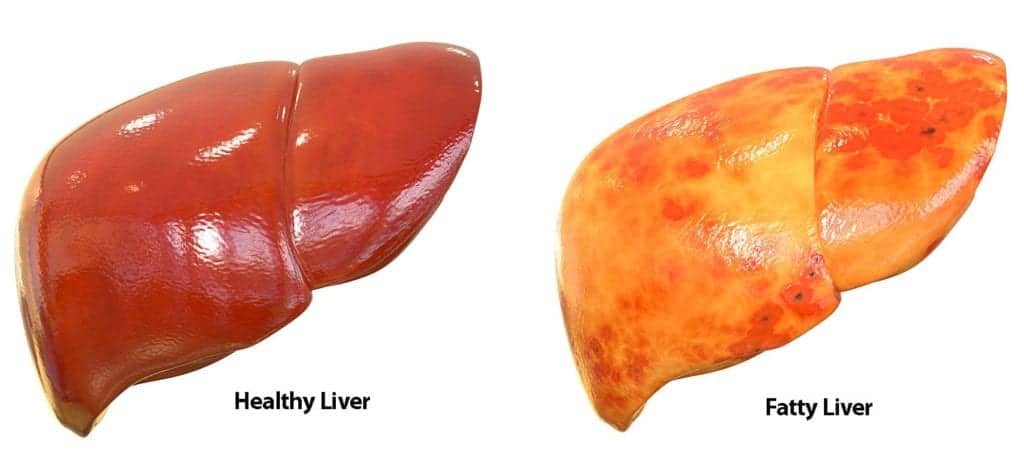
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, medically known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver. While it’s normal for the liver to contain some fat, when fat accounts for more than 5-10% of the liver’s weight, it’s considered fatty liver disease. This condition can be broadly categorized into two main types: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD).
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD is the most common form of fatty liver disease and is not related to alcohol consumption. It typically occurs in individuals who have metabolic risk factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from simple fatty liver (steatosis) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and liver cell damage. NASH can progress to more severe liver complications, including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer;
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption and is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. It represents the early stage of alcohol-related liver disease and can progress to more severe conditions such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis if alcohol intake continues unabated. The risk of developing AFLD is closely linked to the amount and duration of alcohol consumption.
If you have concerns about your liver health or suspect you may have fatty liver disease, consult your healthcare provider for evaluation and guidance.
What is Prozac
Prozac, also known by its generic name fluoxetine, is a medication primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, bulimia nervosa (an eating disorder), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). It belongs to a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter, in the brain. This helps to alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
Prozac is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid, and it is typically taken orally once daily. It is important to use Prozac only as prescribed by a healthcare professional, as misuse or abrupt discontinuation can lead to adverse effects and withdrawal symptoms.
The Link Between Prozac and Fatty Liver
The potential link between Prozac (fluoxetine) and fatty liver disease has been a topic of interest and concern in medical research. While the exact nature of this relationship is still not fully understood, several studies have explored the potential impact of Prozac on liver health.
- Metabolism in the Liver One key factor contributing to the discussion is how Prozac is metabolized in the body. Like many medications, Prozac undergoes metabolism in the liver. The liver plays a crucial role in breaking down drugs and toxins, and the metabolic process can sometimes affect liver function;
- Limited Clinical Evidence: While some studies have suggested a potential association between Prozac use and fatty liver disease, the evidence remains limited and inconclusive. For example, a study published in the journal Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology in 2016 indicated that fluoxetine, the active ingredient in Prozac, could potentially disrupt lipid metabolism in the liver, leading to fatty liver disease. However, further research is needed to confirm and elucidate this connection;
- Other Factors at Play:It’s essential to recognize that fatty liver disease can have causes, including obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications. Untangling the specific contribution of Prozac to the development or progression of fatty liver disease amidst these other factors presents a significant challenge;
- Individual Variability: Moreover, individual differences in metabolism and susceptibility to liver-related side effects may influence the likelihood of experiencing adverse effects from Prozac. Factors such as age, underlying health conditions, genetics, and concurrent use of other medications can all play a role in how the liver responds to Prozac;
- Clinical Monitoring: Given the potential for Prozac to impact liver function, healthcare providers may recommend monitoring liver enzymes through blood tests, especially in individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or risk factors for fatty liver disease. This proactive approach allows for early detection of any abnormalities and appropriate management strategies if needed;
- Patient Education and Awareness: For individuals prescribed Prozac, it’s essential to be aware of potential side effects and to communicate openly with healthcare providers about any concerns or changes in health status. Understanding the risks and benefits of Prozac treatment, as well as adopting a healthy lifestyle, can help mitigate potential adverse effects on liver health.
In conclusion, while the link between Prozac and fatty liver disease warrants consideration and further investigation, it’s important to approach the topic with caution and an awareness of the limitations of current evidence. Healthcare providers and patients alike should remain vigilant, prioritize open communication, and collaborate to ensure optimal treatment outcomes while minimizing potential risks to liver health.
Risks and Considerations:
Individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or risk factors for fatty liver disease, such as obesity, diabetes, or high cholesterol, should exercise caution when taking Prozac. It’s crucial to discuss any concerns or existing health conditions with a healthcare professional before starting or continuing Prozac treatment. Additionally, regular monitoring of liver function through blood tests may be recommended for those taking Prozac long-term.
Prevention Strategies:
While the exact mechanisms underlying the potential link between Prozac and fatty liver disease remain unclear, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding the use of tobacco products. Individuals taking Prozac should also follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations closely and attend regular check-ups to monitor liver health.
Management Options
If fatty liver disease is diagnosed, treatment and management strategies will depend on the severity of the condition and underlying causes. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and dietary changes, may be sufficient to improve liver health. However, more advanced cases may require medication or other interventions to manage symptoms and prevent complications. It’s essential for individuals with fatty liver disease to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion
While further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between Prozac and fatty liver disease, it’s essential for individuals taking this medication to be aware of potential risks and take proactive steps to protect their liver health. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying informed, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can minimize the risk of developing fatty liver disease and ensure their overall well-being.
Remember, if you have any concerns or questions about Prozac and its potential effects on your liver health, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance and support. Your health and well-being are paramount, and your healthcare team is here to help you every step of the way.