Enhancing Liver Health with Probiotics
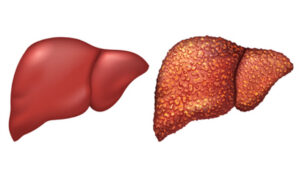
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly recognized as a significant health concern worldwide. It is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver in individuals who consume little to no alcohol. NAFLD can progress to more severe liver conditions, making its prevention and management crucial.
The Crucial Role of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, has emerged as a key factor in the development and progression of NAFLD. These microorganisms play a vital role in digestion, immune function, and overall health. A balanced gut microbiome is linked to numerous health benefits, including robust immune, cardiovascular, and neurological functions.
Imbalance and Its Implications
However, an imbalanced gut microbiome, characterized by a disruption in the microbial community, has been associated with various health issues. Research from 2015 has shown that such imbalances can lead to conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, and notably, liver diseases such as NAFLD.
The Potential of Probiotics in NAFLD Management
Probiotics, live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed, have been identified as a potential tool in managing and preventing NAFLD. These benefits stem from probiotics’ ability to restore balance to the gut microbiome.
Evidence Supporting Probiotic Use
Recent studies suggest that probiotics can significantly impact liver health by improving liver enzyme levels, reducing insulin resistance, and aiding in the regulation of lipid metabolism. This, in turn, can lead to a reduction in liver inflammation and a slowdown in the progression of NAFLD.
Ongoing Research and Promising Outcomes
While research is ongoing to determine the most effective probiotic strains, dosage, and treatment duration, early evidence is promising. Probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have shown potential benefits in managing NAFLD, with some studies recommending their use once or twice daily over an extended period for maximum benefit.
Lifestyle Modifications: A Pillar in NAFLD Management
In addition to probiotic therapy, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing NAFLD. These include:
Regular Exercise and Nutrient-Dense Diet
Engaging in regular physical activity and consuming a diet rich in nutrients are fundamental steps in reducing liver fat. These habits not only aid in weight management but also improve overall liver health. Exercise enhances metabolism and helps decrease insulin resistance, a common issue in NAFLD. A nutrient-dense diet, high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, supports liver function and reduces inflammation. Foods such as leafy greens, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats should be staples. Avoiding processed foods, high in sugar and unhealthy fats, is equally important. Together, these lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk factors associated with NAFLD and promote a healthier liver.
Weight Management Strategies
For individuals with overweight or obesity, the NIDDK recommends losing approximately 3–5% of body weight to reduce liver fat. This should be achieved through gradual weight loss to avoid potential adverse effects on liver health. Rapid weight loss can lead to malnutrition and worsen liver damage, making steady, sustainable weight loss through balanced diet and exercise the preferred approach. In addition to dietary changes, incorporating regular physical activity can enhance weight loss efforts and improve liver enzymes. Weight management is a crucial component of NAFLD treatment, as even modest reductions in body weight can significantly improve liver health and function, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to managing this condition.
Reducing Sedentary Behavior and Alcohol Consumption
Limiting sedentary time and avoiding alcohol are also crucial in managing NAFLD. These changes can significantly impact liver health and prevent further disease progression. Sedentary behavior increases the risk of developing obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases, all of which can exacerbate NAFLD. Incorporating small changes, like standing desks, taking regular breaks for walking, or engaging in leisure activities that involve physical movement, can make a substantial difference. Alcohol, even in small amounts, can cause liver inflammation and damage, worsening NAFLD. Eliminating or significantly reducing alcohol intake is essential for liver health, reducing the risk of further liver complications and supporting overall well-being.
The Importance of Medical Guidance
Before starting any new treatment or making significant lifestyle changes, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential. This ensures that any interventions are appropriate for the individual’s specific health needs and conditions. Medical professionals can provide tailored advice, considering the complexity of NAFLD and any other underlying health issues. They can also monitor progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Collaboration with healthcare providers ensures a comprehensive approach to managing NAFLD, addressing not only the liver condition but also the overall health of the individual, maximizing the effectiveness of treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Conclusion
While NAFLD presents significant health challenges, the emerging research on probiotics and the importance of lifestyle modifications offer hope. By understanding the role of the gut microbiome in liver health and taking proactive steps under medical guidance, individuals can manage or even prevent NAFLD. As research continues to evolve, it is likely that more targeted strategies will become available, further enhancing the ability to combat this prevalent disease.
FAQs:
No, probiotics alone cannot cure NAFLD. While they are a beneficial tool in managing the condition by promoting a healthier gut microbiome, which in turn can positively impact liver health, they are not a standalone cure. Effective management of NAFLD typically requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, increased physical activity, weight management, and in some cases, medication. The synergy of a healthy lifestyle and probiotic supplementation can support liver health and potentially slow the disease’s progression. It is crucial for individuals with NAFLD to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses all aspects of their health, ensuring the best possible outcomes in managing or even reversing NAFLD.
The timeframe for observing significant improvements in NAFLD from probiotic use can vary widely among individuals. While studies suggest that benefits can be seen with consistent use over a period longer than 12 weeks, the exact timing can depend on various factors including the severity of NAFLD, the strains of probiotics used, and adherence to additional lifestyle modifications. Probiotics work by influencing the gut-liver axis, and improvements in liver function tests, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profiles may gradually occur as the gut microbiome becomes more balanced. Continuous evaluation by a healthcare provider is crucial to assess the effectiveness of probiotics in the context of an overall treatment plan for NAFLD. Adjustments to the regimen may be needed based on the individual’s response to therapy.
While probiotics are generally safe and well-tolerated by most individuals, they can cause mild digestive symptoms such as gas, bloating, or discomfort, particularly during the initial stages of supplementation. These symptoms usually resolve on their own as the body adjusts to the new microbial balance. However, it’s essential for individuals with NAFLD to consult with a healthcare provider before starting probiotics, as the condition may require a tailored approach to treatment. People with compromised immune systems, critical illness, or severe underlying health conditions should exercise caution and seek medical advice, as probiotics could pose risks in these populations. Monitoring and guidance from a healthcare professional can help mitigate potential side effects and ensure that probiotic supplementation is a beneficial part of managing NAFLD.